
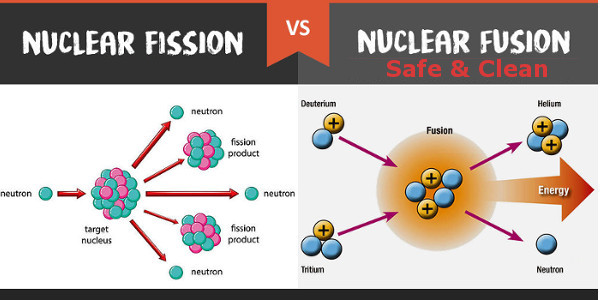
The long range Coulomb repulsion between the nuclei is offset by the stronger but short range attractive strong nuclear force. Compare that to the energy being released in the D-T reaction shown to the right, which at 17 MeV is over 1,000,000 times greater.Ī substantial energy barrier opposes the fusion reaction. For example, the ionization energy gained by adding an electron to hydrogen is 13.6 eV. Thus the energy released in most nuclear reactions is much larger than that for chemical reaction. The total energy contained in a nucleus, the so-called binding energy, is considerably greater than the energy that binds the electrons to the nucleus. This is not the case with fusion, where the lowest mass nucleon, hydrogen, still requires considerable energy to fuse. Unlike fusion however, fission reactions require so little extra energy for very heavy nuclei that they occur all the time on their own. The opposite case, heavy nuclei with too few neutrons, is also unstable and leads to nuclear fission. Most lighter nuclei will return more energy that it requires to cause them to fuse, making the reaction exothermic, generating net power. When lighter nuclei fuse, the resulting nucleon has too many neutrons to be stable, and the neutron is ejected with high energy. Nuclear fusion is the energy source which causes stars to "shine", and hydrogen bombs to explode.Īny two nuclei can be forced to fuse with enough energy.

In physics, nuclear fusion (a thermonuclear reaction) is a process in which two nuclei join to form a larger nucleus, thereby giving off energy.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
